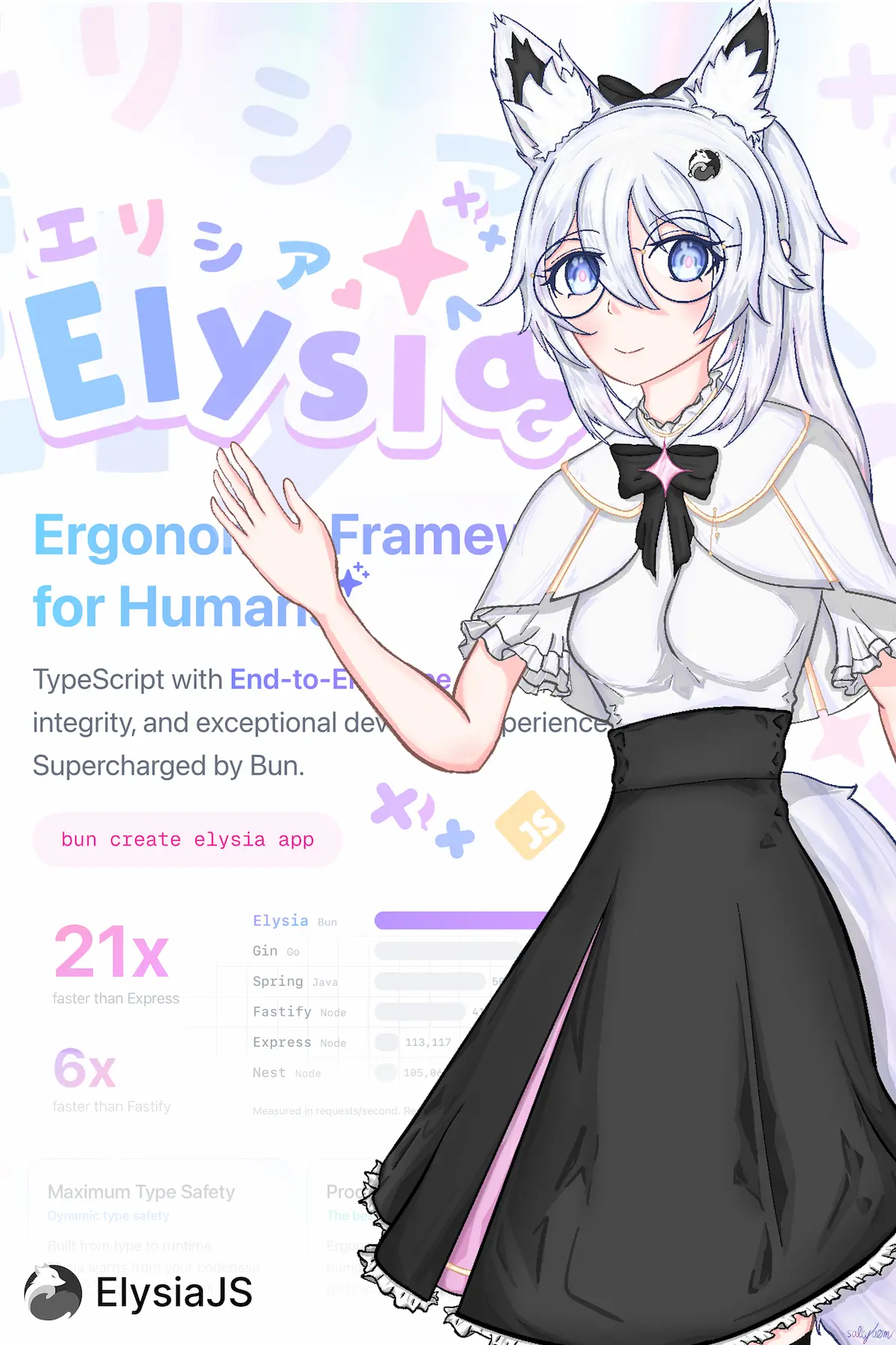
Elysia
2,454,631 reqs/sFastify
415,600
Measured in requests/second. Result from TechEmpower Benchmark Round 22 (2023-10-17) in PlainText
이 가이드는 Fastify 사용자가 구문을 포함한 Fastify와의 차이점을 보고 예제를 통해 Fastify에서 Elysia로 애플리케이션을 마이그레이션하는 방법을 알고 싶어하는 분들을 위한 것입니다.
Fastify는 Node.js를 위한 빠르고 오버헤드가 낮은 웹 프레임워크로, 간단하고 사용하기 쉽게 설계되었습니다. HTTP 모듈 위에 구축되어 웹 애플리케이션을 쉽게 구축할 수 있는 기능 세트를 제공합니다.
Elysia는 Web Standard API를 지원하는 Bun, Node.js 및 런타임을 위한 인체공학적 웹 프레임워크입니다. 건전한 타입 안전성과 성능에 중점을 두고 인체공학적이며 개발자 친화적으로 설계되었습니다.
Elysia는 네이티브 Bun 구현과 정적 코드 분석 덕분에 Fastify보다 훨씬 향상된 성능을 제공합니다.
415,600
Measured in requests/second. Result from TechEmpower Benchmark Round 22 (2023-10-17) in PlainText
Fastify와 Elysia는 유사한 라우팅 구문을 가지고 있으며, app.get() 및 app.post() 메서드를 사용하여 라우트를 정의하고 유사한 경로 매개변수 구문을 사용합니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
const app = fastify()
app.get('/', (request, reply) => {
res.send('Hello World')
})
app.post('/id/:id', (request, reply) => {
reply.status(201).send(req.params.id)
})
app.listen({ port: 3000 })Fastify는 요청 및 응답 객체로
request와reply를 사용합니다
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
.get('/', 'Hello World')
.post(
'/id/:id',
({ status, params: { id } }) => {
return status(201, id)
}
)
.listen(3000)Elysia는 단일
context를 사용하고 응답을 직접 반환합니다
스타일 가이드에 약간의 차이가 있으며, Elysia는 메서드 체이닝과 객체 구조 분해 사용을 권장합니다.
또한 Elysia는 컨텍스트를 사용할 필요가 없는 경우 응답에 대한 인라인 값을 지원합니다.
둘 다 headers, query, params, body와 같은 입력 매개변수에 액세스하기 위한 유사한 속성을 가지고 있으며 요청 본문을 JSON, URL 인코딩 데이터 및 formdata로 자동 파싱합니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
const app = fastify()
app.post('/user', (request, reply) => {
const limit = request.query.limit
const name = request.body.name
const auth = request.headers.authorization
reply.send({ limit, name, auth })
})Fastify는 데이터를 파싱하여
request객체에 넣습니다
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
.post('/user', (ctx) => {
const limit = ctx.query.limit
const name = ctx.body.name
const auth = ctx.headers.authorization
return { limit, name, auth }
})Elysia는 데이터를 파싱하여
context객체에 넣습니다
Fastify는 함수 콜백을 사용하여 서브라우터를 정의하는 반면, Elysia는 모든 인스턴스를 함께 플러그 앤 플레이할 수 있는 컴포넌트로 취급합니다.
import fastify, { FastifyPluginCallback } from 'fastify'
const subRouter: FastifyPluginCallback = (app, opts, done) => {
app.get('/user', (request, reply) => {
reply.send('Hello User')
})
}
const app = fastify()
app.register(subRouter, {
prefix: '/api'
})Fastify는 함수 콜백을 사용하여 서브 라우터를 선언합니다
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const subRouter = new Elysia({ prefix: '/api' })
.get('/user', 'Hello User')
const app = new Elysia()
.use(subRouter)Elysia는 모든 인스턴스를 컴포넌트로 취급합니다
Elysia는 생성자에서 접두사를 설정하는 반면, Fastify는 옵션에서 접두사를 설정해야 합니다.
Elysia는 TypeBox를 사용하여 건전한 타입 안전성과 함께 요청 유효성 검사를 기본적으로 지원하는 반면, Fastify는 스키마 선언에 JSON Schema를, 유효성 검사에 ajv를 사용합니다.
그러나 타입을 자동으로 추론하지 않으며, @fastify/type-provider-json-schema-to-ts와 같은 타입 프로바이더를 사용하여 타입을 추론해야 합니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
import { JsonSchemaToTsProvider } from '@fastify/type-provider-json-schema-to-ts'
const app = fastify().withTypeProvider<JsonSchemaToTsProvider>()
app.patch(
'/user/:id',
{
schema: {
params: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
id: {
type: 'string',
pattern: '^[0-9]+$'
}
},
required: ['id']
},
body: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
name: { type: 'string' }
},
required: ['name']
},
}
},
(request, reply) => {
// map string to number
request.params.id = +request.params.id
reply.send({
params: request.params,
body: request.body
})
}
)Fastify는 유효성 검사에 JSON Schema를 사용합니다
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
.patch('/user/:id', ({ params, body }) => ({
params,
body
}),
{
params: t.Object({
id: t.Number()
}),
body: t.Object({
name: t.String()
})
})import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
import { z } from 'zod'
const app = new Elysia()
.patch('/user/:id', ({ params, body }) => ({
params,
body
}),
{
params: z.object({
id: z.number()
}),
body: z.object({
name: z.string()
})
})import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
import * as v from 'zod'
const app = new Elysia()
.patch('/user/:id', ({ params, body }) => ({
params,
body
}),
{
params: v.object({
id: v.number()
}),
body: v.object({
name: v.string()
})
})Elysia는 유효성 검사에 TypeBox를 사용하고 타입을 자동으로 강제 변환합니다. Zod, Valibot과 같은 다양한 유효성 검사 라이브러리도 동일한 구문으로 지원합니다.
또는 Fastify는 @fastify/type-provider-typebox를 사용하여 타입을 자동으로 추론하기 위해 TypeBox 또는 Zod를 유효성 검사에 사용할 수도 있습니다.
Elysia는 유효성 검사에 TypeBox를 선호하지만, Elysia는 Zod, Valibot, ArkType, Effect Schema 등의 라이브러리를 기본적으로 사용할 수 있도록 Standard Schema를 지원합니다.
Fastify는 Busboy를 사용하는 fastify-multipart를 사용하여 파일 업로드를 처리하는 반면, Elysia는 선언적 API를 사용하여 formdata 및 mimetype 유효성 검사를 처리하기 위해 Web Standard API를 사용합니다.
그러나 Fastify는 파일 크기 및 mimetype과 같은 파일 유효성 검사를 위한 직접적인 방법을 제공하지 않으며, 파일을 유효성 검사하기 위해 일부 해결 방법이 필요합니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
import multipart from '@fastify/multipart'
import { fileTypeFromBuffer } from 'file-type'
const app = fastify()
app.register(multipart, {
attachFieldsToBody: 'keyValues'
})
app.post(
'/upload',
{
schema: {
body: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
file: { type: 'object' }
},
required: ['file']
}
}
},
async (req, res) => {
const file = req.body.file
if (!file) return res.status(422).send('No file uploaded')
const type = await fileTypeFromBuffer(file)
if (!type || !type.mime.startsWith('image/'))
return res.status(422).send('File is not a valid image')
res.header('Content-Type', type.mime)
res.send(file)
}
)Fastify는 파일 업로드를 처리하기 위해
fastify-multipart를 사용하고, Buffer를 허용하기 위해 가짜type: object를 사용합니다
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
.post('/upload', ({ body }) => body.file, {
body: t.Object({
file: t.File({
type: 'image'
})
})
})Elysia는
t.File을 사용하여 파일 및 mimetype 유효성 검사를 처리합니다
multer가 mimetype을 유효성 검사하지 않으므로 file-type 또는 유사한 라이브러리를 사용하여 mimetype을 수동으로 유효성 검사해야 합니다.
Elysia는 파일 업로드를 유효성 검사하고 file-type을 사용하여 mimetype을 자동으로 유효성 검사합니다.
Fastify와 Elysia 모두 이벤트 기반 접근 방식을 사용하여 유사한 라이프사이클 이벤트를 가지고 있습니다.
Elysia의 라이프 사이클 이벤트는 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있습니다.
이미지를 클릭하여 확대
Fastify의 라이프 사이클 이벤트는 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있습니다.
Incoming Request
│
└─▶ Routing
│
└─▶ Instance Logger
│
4**/5** ◀─┴─▶ onRequest Hook
│
4**/5** ◀─┴─▶ preParsing Hook
│
4**/5** ◀─┴─▶ Parsing
│
4**/5** ◀─┴─▶ preValidation Hook
│
400 ◀─┴─▶ Validation
│
4**/5** ◀─┴─▶ preHandler Hook
│
4**/5** ◀─┴─▶ User Handler
│
└─▶ Reply
│
4**/5** ◀─┴─▶ preSerialization Hook
│
└─▶ onSend Hook
│
4**/5** ◀─┴─▶ Outgoing Response
│
└─▶ onResponse Hook둘 다 요청 및 응답 라이프사이클 이벤트를 가로채는 유사한 구문을 가지고 있지만, Elysia는 라이프사이클 이벤트를 계속하기 위해 done을 호출할 필요가 없습니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
const app = fastify()
// Global middleware
app.addHook('onRequest', (request, reply, done) => {
console.log(`${request.method} ${request.url}`)
done()
})
app.get(
'/protected',
{
// Route-specific middleware
preHandler(request, reply, done) {
const token = request.headers.authorization
if (!token) reply.status(401).send('Unauthorized')
done()
}
},
(request, reply) => {
reply.send('Protected route')
}
)Fastify는 미들웨어를 등록하기 위해
addHook을 사용하며, 라이프사이클 이벤트를 계속하기 위해done을 호출해야 합니다
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
// Global middleware
.onRequest(({ method, path }) => {
console.log(`${method} ${path}`)
})
// Route-specific middleware
.get('/protected', () => 'protected', {
beforeHandle({ status, headers }) {
if (!headers.authorizaton)
return status(401)
}
})Elysia는 라이프사이클 이벤트를 자동으로 감지하며, 라이프사이클 이벤트를 계속하기 위해
done을 호출할 필요가 없습니다
Elysia는 건전한 타입 안전성을 위해 설계되었습니다.
예를 들어, derive 및 resolve를 사용하여 타입 안전 방식으로 컨텍스트를 커스터마이즈할 수 있지만 Fastify는 그렇지 않습니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
const app = fastify()
app.decorateRequest('version', 2)
app.get('/version', (req, res) => {
res.send(req.version)Property 'version' does not exist on type 'FastifyRequest<RouteGenericInterface, Server<typeof IncomingMessage, typeof ServerResponse>, IncomingMessage, ... 4 more ..., ResolveFastifyRequestType<...>>'.})
app.get(
'/token',
{
preHandler(req, res, done) {
const token = req.headers.authorization
if (!token) return res.status(401).send('Unauthorized')
// @ts-ignore
req.token = token.split(' ')[1]
done()
}
},
(req, res) => {
req.versionProperty 'version' does not exist on type 'FastifyRequest<RouteGenericInterface, Server<typeof IncomingMessage, typeof ServerResponse>, IncomingMessage, ... 4 more ..., ResolveFastifyRequestType<...>>'.
res.send(req.token)Property 'token' does not exist on type 'FastifyRequest<RouteGenericInterface, Server<typeof IncomingMessage, typeof ServerResponse>, IncomingMessage, ... 4 more ..., ResolveFastifyRequestType<...>>'. }
)
app.listen({
port: 3000
})Fastify는
decorateRequest를 사용하지만 건전한 타입 안전성을 제공하지 않습니다
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
.decorate('version', 2)
.get('/version', ({ version }) => version)
.resolve(({ status, headers: { authorization } }) => {
if(!authorization?.startsWith('Bearer '))
return status(401)
return {
token: authorization.split(' ')[1]
}
})
.get('/token', ({ token, version }) => {
version
return token
})Elysia는 컨텍스트를 확장하기 위해
decorate를 사용하고, 컨텍스트에 사용자 정의 속성을 추가하기 위해resolve를 사용합니다
Fastify는 declare module을 사용하여 FastifyRequest 인터페이스를 확장할 수 있지만, 전역적으로 사용 가능하며 건전한 타입 안전성을 가지지 않고 모든 요청 핸들러에서 속성이 사용 가능한지 보장하지 않습니다.
declare module 'fastify' {
interface FastifyRequest {
version: number
token: string
}
}위의 Fastify 예제가 작동하려면 이것이 필요하지만, 건전한 타입 안전성을 제공하지 않습니다
Fastify는 명명된 미들웨어를 정의하기 위해 Fastify 플러그인을 반환하는 함수를 사용하는 반면, Elysia는 사용자 정의 후크를 정의하기 위해 macro를 사용합니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
import type { FastifyRequest, FastifyReply } from 'fastify'
const app = fastify()
const role =
(role: 'user' | 'admin') =>
(request: FastifyRequest, reply: FastifyReply, next: Function) => {
const user = findUser(request.headers.authorization)
if (user.role !== role) return reply.status(401).send('Unauthorized')
// @ts-ignore
request.user = user
next()
}
app.get(
'/token',
{
preHandler: role('admin')
},
(request, reply) => {
reply.send(request.user)Property 'user' does not exist on type 'FastifyRequest<RouteGenericInterface, Server<typeof IncomingMessage, typeof ServerResponse>, IncomingMessage, ... 4 more ..., ResolveFastifyRequestType<...>>'. }
)Fastify는 미들웨어에 대한 사용자 정의 인수를 허용하기 위해 함수 콜백을 사용합니다
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia()
.macro({
role: (role: 'user' | 'admin') => ({
resolve({ status, headers: { authorization } }) {
const user = findUser(authorization)
if(user.role !== role)
return status(401)
return {
user
}
}
})
})
.get('/token', ({ user }) => user, {
role: 'admin'
})Elysia는 사용자 정의 미들웨어에 사용자 정의 인수를 전달하기 위해 매크로를 사용합니다
Fastify는 함수 콜백을 사용하지만, 이벤트 핸들러에 배치할 함수 또는 후크로 표현된 객체를 반환해야 합니다. 여러 사용자 정의 함수가 필요한 경우 이들을 단일 객체로 조정해야 하므로 처리하기 어려울 수 있습니다.
Fastify와 Elysia 모두 오류를 처리하기 위한 라이프사이클 이벤트를 제공합니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
const app = fastify()
class CustomError extends Error {
constructor(message: string) {
super(message)
this.name = 'CustomError'
}
}
// global error handler
app.setErrorHandler((error, request, reply) => {
if (error instanceof CustomError)
reply.status(500).send({
message: 'Something went wrong!',
error
})
})
app.get(
'/error',
{
// route-specific error handler
errorHandler(error, request, reply) {
reply.send({
message: 'Only for this route!',
error
})
}
},
(request, reply) => {
throw new CustomError('oh uh')
}
)Fastify는 전역 오류 핸들러에
setErrorHandler를, 라우트별 오류 핸들러에errorHandler를 사용합니다
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
class CustomError extends Error {
// Optional: custom HTTP status code
status = 500
constructor(message: string) {
super(message)
this.name = 'CustomError'
}
// Optional: what should be sent to the client
toResponse() {
return {
message: "If you're seeing this, our dev forgot to handle this error",
error: this
}
}
}
const app = new Elysia()
// Optional: register custom error class
.error({
CUSTOM: CustomError,
})
// Global error handler
.onError(({ error, code }) => {
if(code === 'CUSTOM')
return {
message: 'Something went wrong!',
error
}
})
.get('/error', () => {
throw new CustomError('oh uh')
}, {
// Optional: route specific error handler
error({ error }) {
return {
message: 'Only for this route!',
error
}
}
})Elysia는 상태에 대한 약칭과 오류를 응답에 매핑하기 위한
toResponse와 함께 사용자 정의 오류 코드를 제공합니다.
둘 다 라이프사이클 이벤트를 사용하여 오류 처리를 제공하지만, Elysia는 다음을 제공합니다:
toResponse오류 코드는 로깅 및 디버깅에 유용하며, 동일한 클래스를 확장하는 다른 오류 유형을 구별할 때 중요합니다.
Elysia는 타입 안전성과 함께 이 모든 것을 제공하지만 Fastify는 그렇지 않습니다.
Fastify는 플러그인 부작용을 캡슐화하는 반면, Elysia는 명시적 범위 지정 메커니즘 및 코드 순서를 통해 플러그인의 부작용을 제어할 수 있습니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
import type { FastifyPluginCallback } from 'fastify'
const subRouter: FastifyPluginCallback = (app, opts, done) => {
app.addHook('preHandler', (request, reply) => {
if (!request.headers.authorization?.startsWith('Bearer '))
reply.code(401).send({ error: 'Unauthorized' })
})
done()
}
const app = fastify()
.get('/', (request, reply) => {
reply.send('Hello World')
})
.register(subRouter)
// doesn't have side-effect from subRouter
.get('/side-effect', () => 'hi')Fastify는 플러그인의 부작용을 캡슐화합니다
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const subRouter = new Elysia()
.onBeforeHandle(({ status, headers: { authorization } }) => {
if(!authorization?.startsWith('Bearer '))
return status(401)
})
const app = new Elysia()
.get('/', 'Hello World')
.use(subRouter)
// doesn't have side-effect from subRouter
.get('/side-effect', () => 'hi')Elysia는 명시적으로 지정하지 않는 한 플러그인의 부작용을 캡슐화합니다
둘 다 부작용을 방지하기 위한 플러그인의 캡슐화 메커니즘을 가지고 있습니다.
그러나 Elysia는 범위를 선언하여 어떤 플러그인이 부작용을 가져야 하는지 명시적으로 지정할 수 있지만 Fastify는 항상 캡슐화합니다.
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const subRouter = new Elysia()
.onBeforeHandle(({ status, headers: { authorization } }) => {
if(!authorization?.startsWith('Bearer '))
return status(401)
})
// Scoped to parent instance but not beyond
.as('scoped')
const app = new Elysia()
.get('/', 'Hello World')
.use(subRouter)
// now have side-effect from subRouter
.get('/side-effect', () => 'hi')Elysia는 3가지 유형의 범위 지정 메커니즘을 제공합니다:
Fastify는 범위 지정 메커니즘을 제공하지 않으므로 다음 중 하나를 수행해야 합니다:
그러나 주의하지 않으면 중복된 부작용이 발생할 수 있습니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
import type {
FastifyRequest,
FastifyReply,
FastifyPluginCallback
} from 'fastify'
const log = (request: FastifyRequest, reply: FastifyReply, done: Function) => {
console.log('Middleware executed')
done()
}
const app = fastify()
app.addHook('onRequest', log)
app.get('/main', (request, reply) => {
reply.send('Hello from main!')
})
const subRouter: FastifyPluginCallback = (app, opts, done) => {
app.addHook('onRequest', log)
// This would log twice
app.get('/sub', (request, reply) => {
return reply.send('Hello from sub router!')
})
done()
}
app.register(subRouter, {
prefix: '/sub'
})
app.listen({
port: 3000
})이 시나리오에서 Elysia는 중복된 부작용을 방지하기 위한 플러그인 중복 제거 메커니즘을 제공합니다.
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const subRouter = new Elysia({ name: 'subRouter' })
.onBeforeHandle(({ status, headers: { authorization } }) => {
if(!authorization?.startsWith('Bearer '))
return status(401)
})
.as('scoped')
const app = new Elysia()
.get('/', 'Hello World')
.use(subRouter)
.use(subRouter)
.use(subRouter)
.use(subRouter)
// side-effect only called once
.get('/side-effect', () => 'hi')고유한 name을 사용하면 Elysia는 플러그인을 한 번만 적용하고 중복된 부작용을 일으키지 않습니다.
Fastify는 쿠키를 파싱하기 위해 @fastify/cookie를 사용하는 반면, Elysia는 쿠키를 처리하기 위해 시그널 기반 접근 방식을 내장 지원합니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
import cookie from '@fastify/cookie'
const app = fastify()
app.use(cookie, {
secret: 'secret',
hook: 'onRequest'
})
app.get('/', function (request, reply) {
request.unsignCookie(request.cookies.name)
reply.setCookie('name', 'value', {
path: '/',
signed: true
})
})Fastify는 쿠키 서명을 확인하기 위해
unsignCookie를, 쿠키를 설정하기 위해setCookie를 사용합니다
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
const app = new Elysia({
cookie: {
secret: 'secret'
}
})
.get('/', ({ cookie: { name } }) => {
// signature verification is handle automatically
name.value
// cookie signature is signed automatically
name.value = 'value'
name.maxAge = 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24
})Elysia는 쿠키를 처리하기 위해 시그널 기반 접근 방식을 사용하며, 서명 확인은 자동으로 처리됩니다
둘 다 Swagger를 사용하여 OpenAPI 문서를 제공하지만, Elysia는 OpenAPI 문서를 위한 보다 현대적이고 사용자 친화적인 인터페이스인 Scalar UI를 기본으로 사용합니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
import swagger from '@fastify/swagger'
const app = fastify()
app.register(swagger, {
openapi: '3.0.0',
info: {
title: 'My API',
version: '1.0.0'
}
})
app.addSchema({
$id: 'user',
type: 'object',
properties: {
name: {
type: 'string',
description: 'First name only'
},
age: { type: 'integer' }
},
required: ['name', 'age']
})
app.post(
'/users',
{
schema: {
summary: 'Create user',
body: {
$ref: 'user#'
},
response: {
'201': {
$ref: 'user#'
}
}
}
},
(req, res) => {
res.status(201).send(req.body)
}
)
await fastify.ready()
fastify.swagger()Fastify는 Swagger를 사용한 OpenAPI 문서에
@fastify/swagger를 사용합니다
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
import { openapi } from '@elysiajs/openapi'
const app = new Elysia()
.use(openapi())
.model({
user: t.Array(
t.Object({
name: t.String(),
age: t.Number()
})
)
})
.post('/users', ({ body }) => body, {
body: 'user',
response: {
201: 'user'
},
detail: {
summary: 'Create user'
}
})Elysia는 기본적으로 Scalar를 사용한 OpenAPI 문서에
@elysiajs/swagger를 사용하거나, 선택적으로 Swagger를 사용합니다
둘 다 OpenAPI 문서에 대해 $ref를 사용하여 모델 참조를 제공하지만, Fastify는 타입 안전성 및 모델 이름 지정을 위한 자동 완성을 제공하지 않지만 Elysia는 제공합니다.
Fastify는 네트워크 요청을 시뮬레이션하기 위해 fastify.inject()를 사용하는 테스트를 위한 내장 지원을 가지고 있는 반면, Elysia는 실제 요청을 수행하기 위해 Web Standard API를 사용합니다.
import fastify from 'fastify'
import request from 'supertest'
import { describe, it, expect } from 'vitest'
function build(opts = {}) {
const app = fastify(opts)
app.get('/', async function (request, reply) {
reply.send({ hello: 'world' })
})
return app
}
describe('GET /', () => {
it('should return Hello World', async () => {
const app = build()
const response = await app.inject({
url: '/',
method: 'GET',
})
expect(res.status).toBe(200)
expect(res.text).toBe('Hello World')
})
})Fastify는 네트워크 요청을 시뮬레이션하기 위해
fastify.inject()를 사용합니다
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
import { describe, it, expect } from 'vitest'
const app = new Elysia()
.get('/', 'Hello World')
describe('GET /', () => {
it('should return Hello World', async () => {
const res = await app.handle(
new Request('http://localhost')
)
expect(res.status).toBe(200)
expect(await res.text()).toBe('Hello World')
})
})Elysia는 실제 요청을 처리하기 위해 Web Standard API를 사용합니다
또한 Elysia는 End-to-end 타입 안전성을 위한 Eden이라는 헬퍼 라이브러리를 제공하여 자동 완성 및 완전한 타입 안전성으로 테스트할 수 있습니다.
import { Elysia } from 'elysia'
import { treaty } from '@elysiajs/eden'
import { describe, expect, it } from 'bun:test'
const app = new Elysia().get('/hello', 'Hello World')
const api = treaty(app)
describe('GET /', () => {
it('should return Hello World', async () => {
const { data, error, status } = await api.hello.get()
expect(status).toBe(200)
expect(data).toBe('Hello World')
})
})Elysia는 코드 생성 없이 Eden을 사용하여 end-to-end 타입 안전성을 기본적으로 지원하지만, Fastify는 제공하지 않습니다.
import { Elysia, t } from 'elysia'
import { treaty } from '@elysiajs/eden'
const app = new Elysia()
.post('/mirror', ({ body }) => body, {
body: t.Object({
message: t.String()
})
})
const api = treaty(app)
const { data, error } = await api.mirror.post({
message: 'Hello World'
})
if(error)
throw error
console.log(data)
end-to-end 타입 안전성이 중요하다면 Elysia가 올바른 선택입니다.
Elysia는 성능, 타입 안전성 및 단순성에 중점을 두고 보다 인체공학적이고 개발자 친화적인 경험을 제공하는 반면, Fastify는 Node.js를 위한 확립된 프레임워크 중 하나이지만 차세대 프레임워크가 제공하는 건전한 타입 안전성 및 end-to-end 타입 안전성을 가지고 있지 않습니다.
사용하기 쉽고, 훌륭한 개발자 경험을 가지고 있으며, Web Standard API 위에 구축된 프레임워크를 찾고 있다면 Elysia가 올바른 선택입니다.
또는 다른 프레임워크에서 온 경우 다음을 확인할 수 있습니다: